Chinese Humanoid Robot Achieves 130,000 Steps in Extreme -47°C Cold: A Breakthrough in Robotics
World's First: Unitree Humanoid Robot Autonomous Walking Challenge in −47.4°C Extreme Cold
Key Points:
Unitree G1 robot completed 130,000 steps autonomously in subzero temperatures.
Equipped with advanced sensors, BeiDou navigation, and adaptive path-planning.
Marks a new milestone in cold-weather humanoid robotics endurance.
advertisement
Introduction
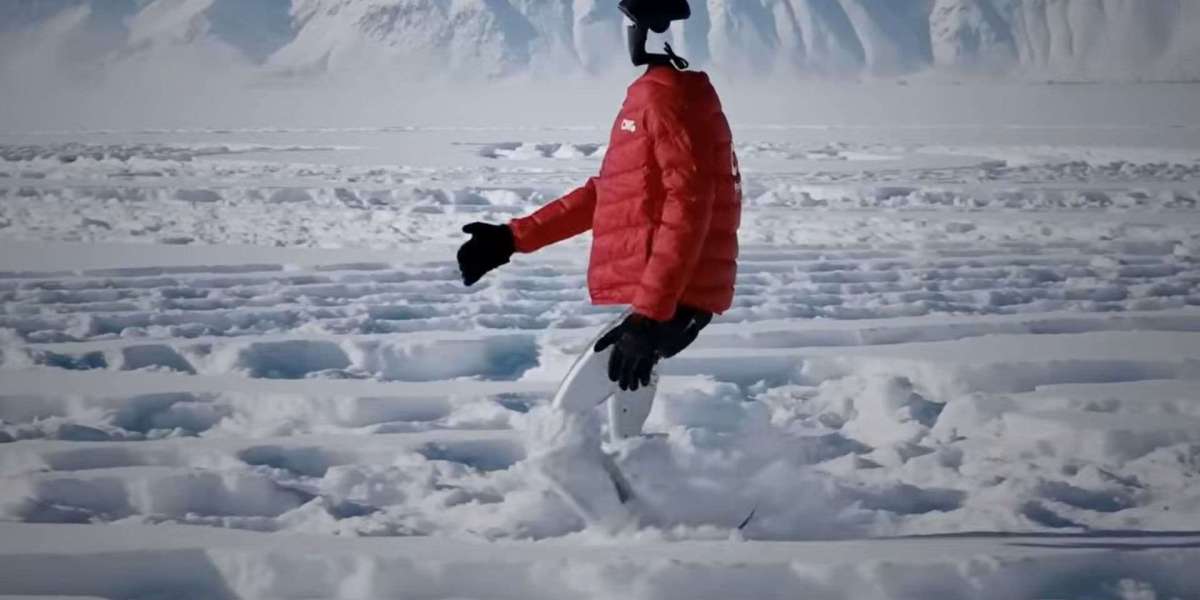
China’s Unitree G1 humanoid robot has made history by walking over 130,000 steps in the freezing temperatures of Xinjiang’s Altay region, reaching as low as –47.4°C (–53°F). In a remarkable demonstration of robotics engineering, the G1 traced a Winter Olympics emblem across a 186 by 100-metre ice field, showcasing the first fully autonomous humanoid walking feat in extreme cold conditions.
Unitree G1: Engineering for Extreme Cold
To survive the harsh winter environment, engineers modified the G1 from its standard factory configuration. The robot donned an orange insulated puffer jacket and plastic protective sleeves over its legs and feet, shielding its joints, actuators, and battery from freezing conditions. This practical adaptation allowed the G1 to maintain continuous movement across icy terrain.
Weighing approximately 35 kilograms (77 pounds) and standing 127 centimetres tall, the G1 features between 23 and 43 joint motors with a maximum torque of 120 newton-metres. Its advanced sensor suite includes 3D LiDAR, Intel RealSense depth cameras, and a microphone array for voice commands. The robot runs on a 9,000 mAh quick-release battery, capable of up to two hours of operation, and is powered by an eight-core processor. Its proprietary UnifoLM system uses reinforcement learning for motion control and task execution, enabling agile walking and speeds of up to 4.5 miles per hour.
advertisement
Precision Navigation and Path Planning
The G1 relied on China’s BeiDou Navigation Satellite System for centimeter-level positioning. Its onboard adaptive path-planning algorithms allowed it to navigate uneven ice surfaces while tracing the emblem accurately. This level of autonomy is a significant leap from most commercial humanoid robots, which are typically designed for indoor or controlled environments.
Global Context and Industry Significance
Unitree, headquartered in Hangzhou, is one of China’s leading robotics firms. Reports indicate the company shipped over 5,500 humanoid robots in 2025 alone, commanding a substantial portion of the global market. Analysts from Omdia and Counterpoint Research have ranked Unitree among the top humanoid manufacturers worldwide.
This demonstration highlights a broader trend in robotics: environmental durability is becoming a competitive benchmark. Rival firms, such as Deep Robotics with their all-weather DR02 platform, are also pursuing robust, weather-resistant designs, though the G1’s extreme cold endurance represents a new frontier in real-world humanoid mobility.
advertisement
Conclusion
The G1’s achievement is not just a technical milestone but a glimpse into the future of humanoid robotics. By demonstrating autonomous walking in extreme cold, Unitree has expanded the boundaries of where and how robots can operate, from icy landscapes to harsh industrial settings. This progress underscores the growing intersection of artificial intelligence, advanced sensor systems, and mechanical engineering, inspiring innovations that may one day make humanoid robots indispensable in environments once thought impossible to navigate.
Key Points Summary:
First humanoid robot to achieve sustained autonomous walking in extreme subzero conditions.
Equipped with advanced sensors, BeiDou navigation, and adaptive path-planning.
Demonstrates the growing importance of environmental durability in robotics.
G1 weighs 35 kg, stands 127 cm tall, with a 9,000 mAh battery and 23–43 joint motors.
Marks a milestone in real-world applications for humanoid AI and robotics technology.
advertisement
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ):
What is the Unitree G1 humanoid robot?
The G1 is a Chinese humanoid robot designed for general-purpose tasks, equipped with sensors, advanced navigation, and AI-based motion control.How many steps did the G1 take in extreme cold?
Over 130,000 steps in temperatures as low as –47.4°C (–53°F).What modifications were made for cold-weather operation?
The robot wore an insulated puffer jacket and plastic leg sleeves to protect joints, actuators, and battery from freezing.What navigation system does the G1 use?
It uses China’s BeiDou Navigation Satellite System for centimeter-level positioning accuracy.How long can the G1 operate on a single battery?
Its 9,000 mAh quick-release battery supports up to two hours of continuous operation.Why is this milestone significant?
It demonstrates the first sustained, fully autonomous walking of a humanoid robot in extreme cold, setting a new benchmark for environmental durability in robotics.
Sources:
VnExpress – Report on Unitree G1 walking 130,000 steps in –47.4°C.
https://e.vnexpress.net/news/tech/tech-news/china-s-humanoid-robot-becomes-first-in-the-world-to-take-130-000-steps-in-47-4-c-5015431.htmlInteresting Engineering – Coverage of Unitree G1’s cold-weather demonstration and technical details.
https://interestingengineering.com/ai-robotics/unitree-humanoid-robot-record-snow-walk
Thank you !