Boiling Sweet Potatoes: Health Benefits, Nutrition, and the Best Way to Cook Them

3 Quick Takeaways
Boiling sweet potatoes helps retain key nutrients like beta-carotene and vitamin C.
This cooking method can significantly lower the glycemic index compared to baking or frying.
Boiled sweet potatoes support gut health and require no added fats or oils.
advertisement
Introduction
Boiling sweet potatoes is often overlooked in favor of roasting or baking, yet it may be one of the healthiest ways to prepare this naturally nutrient-dense vegetable. Sweet potatoes are widely valued for their fiber, antioxidants, and essential vitamins, but how they are cooked can greatly influence their nutritional impact. Research highlighted by Verywell Health shows that boiling sweet potatoes can enhance nutrient retention, improve digestibility, and support stable blood sugar levels, making it a smart choice for everyday meals.
Why Boiling Sweet Potatoes Preserves More Nutrients

Cooking inevitably alters the nutrient profile of vegetables, but boiling sweet potatoes appears to preserve more beneficial compounds than many other cooking methods. According to Verywell Health, boiling sweet potatoes for up to 20 minutes can retain as much as 92% of their beta-carotene content. Beta-carotene, which the body converts into vitamin A, plays a role in supporting vision, immune health, and protection against chronic conditions such as cardiovascular disease and certain cancers.
Boiling also helps maintain vitamin C levels, particularly when the skin is left intact. Additionally, this method can improve the body’s ability to absorb nutrients, meaning the vitamins and minerals present are more effectively utilized.
Key Nutrients Found in Sweet Potatoes
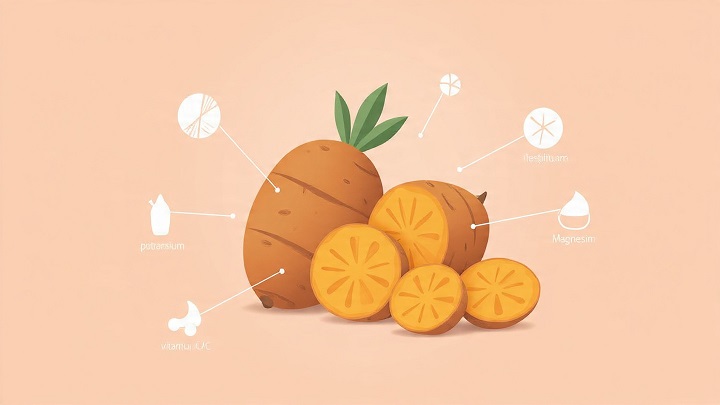

Sweet potatoes offer a broad range of essential nutrients that contribute to overall health. These include calcium, dietary fiber, magnesium, potassium, phosphorus, selenium, zinc, and vitamin C. Together, these nutrients support bone health, digestion, muscle function, and immune resilience.
advertisement
Boiling Sweet Potatoes and Blood Sugar Control
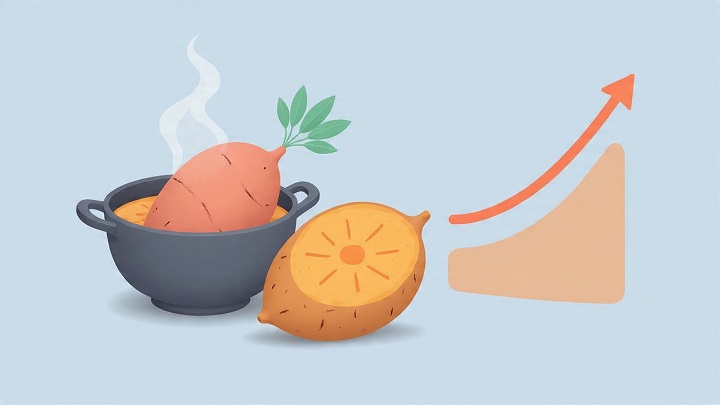

Sweet potatoes are known to have moderate to high glycemic index (GI) values, depending on how they are cooked. The glycemic index measures how quickly a food raises blood sugar levels after consumption. Boiling sweet potatoes can significantly lower their GI compared to frying, baking, or roasting.
Verywell Health reports that while baked or roasted sweet potatoes may reach GI scores as high as 94, boiled sweet potatoes typically range between 46 and 50, depending on the variety. This reduction occurs because boiling alters the chemical structure of the starches, slowing digestion and resulting in a more gradual rise in blood glucose levels. For individuals managing diabetes or aiming for steady energy levels, boiled sweet potatoes may be a better option.
Digestibility, Resistant Starch, and Gut Health
Sweet potatoes contain resistant starch, a type of carbohydrate that functions similarly to dietary fiber by feeding beneficial gut bacteria. The resistant starch content varies by variety but generally falls between 0.3 and 2.1 grams per 100 grams.
Boiling helps preserve resistant starch levels, supporting digestive health and promoting a balanced gut microbiome. According to Verywell Health, diets rich in resistant starch may contribute to improved immunity, mood regulation, heart health, and weight management.
Allowing boiled sweet potatoes to cool before eating can further increase resistant starch levels, enhancing their gut-friendly benefits.
Fewer Added Ingredients, Fewer Health Risks
One of the simplest advantages of boiling sweet potatoes is that it requires only water. Other cooking methods often involve butter, oil, or other fats that increase calorie and saturated fat intake. Verywell Health notes that just one tablespoon of butter adds over 11 grams of fat, including a significant amount of saturated fat.
Excessive saturated fat consumption has been linked to higher cholesterol levels, increased risk of heart disease and stroke, and weight gain. Boiling avoids these concerns while still delivering flavor and nutrition.
How to Maximize the Benefits of Boiled Sweet Potatoes

To get the most out of boiled sweet potatoes, a few practical steps can make a difference. Leaving the skin on helps preserve nutrients, as the peel contains valuable vitamins and antioxidants. Using sweet potatoes within a week of purchase ensures better freshness and nutrient content. Limiting added ingredients allows the natural nutritional profile to shine.
Conclusion

Boiling sweet potatoes is a simple yet powerful way to unlock their full health potential. From preserving beta-carotene and vitamin C to lowering glycemic impact and supporting gut health, this cooking method offers benefits that go beyond convenience. By choosing to boil sweet potatoes, you embrace a preparation style that aligns with balanced nutrition, heart health, and long-term wellness. Sometimes, the healthiest choice is also the simplest one.
Key Points Summary
Boiling preserves more beta-carotene and vitamin C than many other cooking methods.
It lowers the glycemic index, supporting better blood sugar control.
Resistant starch in boiled sweet potatoes promotes gut health.
No added fats are required, reducing saturated fat intake.
advertisement
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Are boiled sweet potatoes healthier than baked ones?
According to Verywell Health, boiled sweet potatoes retain more beta-carotene and have a lower glycemic index than baked sweet potatoes.
Should I peel sweet potatoes before boiling?
Leaving the skin on can help preserve nutrients, including vitamin C and antioxidants.
Do boiled sweet potatoes taste bland?
They have a mild, naturally sweet flavor and can be enhanced with herbs, spices, or healthy toppings after cooking.
Can boiled sweet potatoes help with digestion?
Yes, they contain resistant starch that supports gut bacteria and digestive health.
Does cooling boiled sweet potatoes change their nutrition?
Cooling increases resistant starch levels, which may further benefit gut health and blood sugar control.
Sources
Verywell Health – Health and nutrition insights on boiling sweet potatoes
https://www.verywellhealth.com/boiling-sweet-potatoes-11875552
Thank you !