article image source: NDTV (Link)
For The First Time, Humans Can Watch Plants 'Breathe': The Breakthrough Changing How We Understand Plant Life
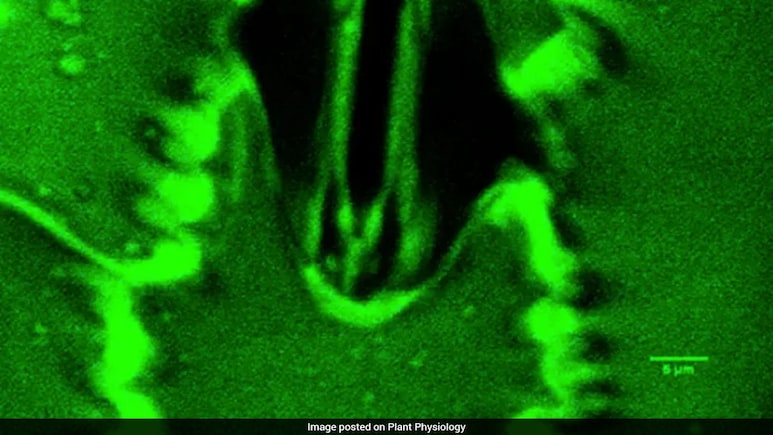
The breakthrough could help unlock crops that grow smarter, stronger, and more drought-resistant.
image source: NDTV
Seeing Plants Breathe
— Brian Roemmele (@BrianRoemmele) January 15, 2026
Researchers have achieved a breakthrough in plant biology by developing a way to watch plants
"breathe" in real time.
While we have known for centuries that plants exchange gases through microscopic pores called stomata, we have never before been able to… pic.twitter.com/j62H8y6mtk
Key Points:
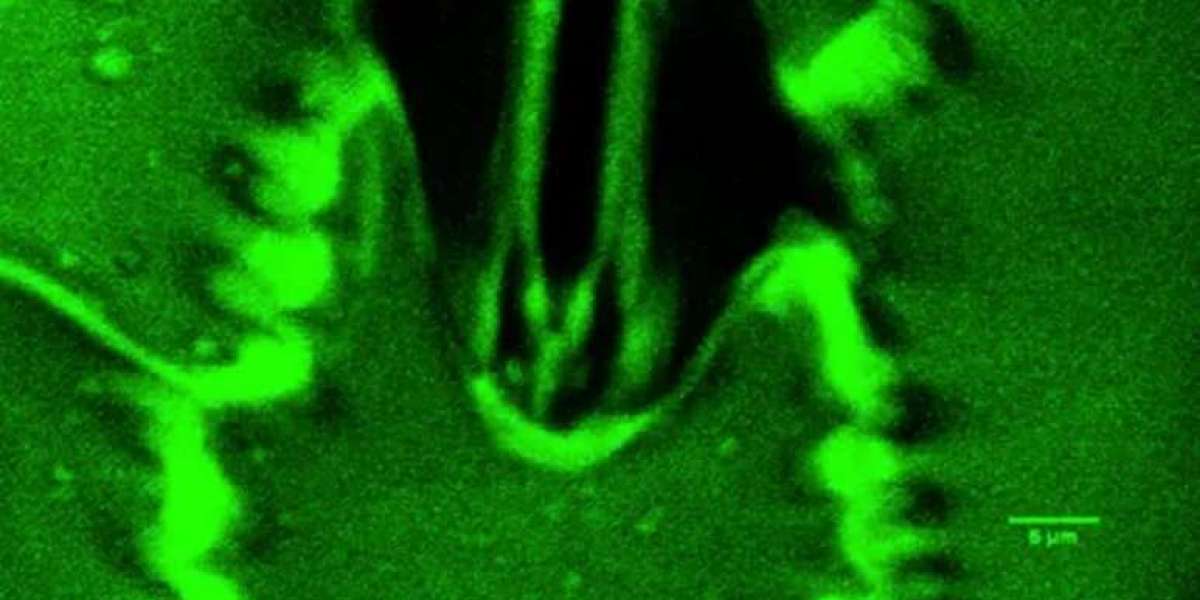
Scientists can now observe stomata—tiny leaf pores—opening and closing in real time.
This technology provides critical insights into water use, photosynthesis, and plant resilience.
Potential to revolutionize crop breeding for drought-resistant and water-efficient plants.
advertisement
Introduction
For centuries, humans have understood that plants "breathe" through microscopic leaf pores called stomata, yet this process remained invisible in real time—until now. Researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have developed a groundbreaking tool, Stomata In-Sight, that allows scientists to observe how plants manage the delicate balance between absorbing carbon dioxide for photosynthesis and conserving water. This breakthrough opens new doors for understanding plant health, crop resilience, and the future of agriculture.
How Plants 'Breathe'
Plants absorb carbon dioxide (CO₂) from the air to fuel photosynthesis, releasing oxygen (O₂) and water vapor in the process. This exchange occurs through stomata—tiny openings on leaf surfaces often described as the plant’s mouths. Traditionally, scientists could measure the overall gas exchange but could not observe the microscopic movement of these pores in real time.
With Stomata In-Sight, researchers can watch stomata open in light to allow photosynthesis and close in darkness or under drought conditions to conserve water. Andrew Leakey of the University of Illinois explains that stomata regulate water loss and gas intake in response to environmental cues, such as light, humidity, temperature, and water availability. Observing these processes in detail provides unprecedented insight into plant survival strategies.
The Technology Behind the Breakthrough
The device combines three advanced systems:
High-resolution confocal microscopy for visualizing microscopic structures.
Precise gas-exchange measurement to track CO₂, O₂, and water vapor.
Machine-learning software for analyzing dynamic stomatal responses.
Leaf samples are placed in a compact, palm-sized chamber where temperature, humidity, light, CO₂ levels, and water availability are controlled. This allows researchers to record videos showing the real-time movement of gases and subtle cellular changes as stomata respond to their environment. Developing this system took nearly five years, overcoming challenges like vibration interference and stability issues.
advertisement
Why This Matters
Understanding stomatal behavior has profound implications for agriculture and environmental sustainability. Water scarcity is one of the biggest constraints on crop production worldwide. By studying how stomata regulate water use, scientists can identify genetic traits that enhance water efficiency and drought resistance in crops.
This knowledge could transform crop breeding strategies, leading to plants that thrive even under rising temperatures and limited water supply. The University of Illinois has patented the technology, and although it is not yet commercially available, the research team aims to make it widely accessible to the scientific community.
Inspiring Outlook for the Future
Watching plants "breathe" is more than a scientific curiosity—it represents a leap forward in our understanding of life on Earth. This innovation has the potential to make agriculture more resilient, conserve water, and help feed a growing global population under increasingly challenging environmental conditions. By revealing the hidden rhythms of plant life, Stomata In-Sight brings humanity closer to harmonizing with nature rather than exploiting it.
Key Points Summary
Scientists observe stomata in real time for the first time.
Technology tracks CO₂ intake, oxygen release, and water vapor loss.
Insight into plant adaptation, water regulation, and crop resilience.
Potential to revolutionize drought-resistant crop breeding.
Developed by University of Illinois, patented, soon available for research.
advertisement
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What are stomata?
A: Stomata are microscopic pores on leaves that allow plants to exchange gases—absorbing CO₂ for photosynthesis while releasing oxygen and water vapor.
Q2: How does Stomata In-Sight work?
A: It combines high-resolution microscopy, precise gas measurements, and machine-learning software to observe and analyze stomatal behavior in real time under controlled conditions.
Q3: Why is this breakthrough important?
A: Observing stomata in real time helps scientists understand water regulation and photosynthesis, enabling the development of drought-resistant and water-efficient crops.
Q4: Can this technology be used commercially?
A: Currently, it is patented and primarily for research, but the team hopes it will be manufactured for broader scientific use.
Q5: How long did it take to develop this system?
A: Nearly five years of refinement were required to create a stable, reliable system capable of observing microscopic stomatal movements.
Sources
NDTV – For the First Time, Humans Can Watch How Plants 'Breathe', Here's Why This Breakthrough Matters
https://www.ndtv.com/science/for-the-first-time-humans-can-watch-how-plants-breathe-heres-why-this-breakthrough-matters-10781677
Thank you !