Salty Ice Electricity Generation: How Salted Ice Can Produce Power in Extreme Environments

Ice that generates electricity may sound impossible, yet recent research shows that salty ice could become a surprising source of clean energy in the world’s coldest places.
3 Key Takeaways at a Glance
Salty ice can generate electricity when bent, thanks to a physical effect called flexoelectricity
Adding salt increases ice’s electrical output by up to 1,000 times compared to pure ice
This discovery could enable energy harvesting and sensors in polar and other extreme environments
advertisement
Introduction: Turning Ice Into a Source of Electricity
For centuries, humans have relied on water to generate power, from ancient watermills to modern hydroelectric dams. Ice, however, has traditionally been viewed as energetically inactive. That assumption is now changing. New research reveals that when ice is mixed with salt and mechanically bent, it can generate measurable electrical energy. This breakthrough opens the door to innovative technologies designed for extreme cold environments, where traditional energy systems struggle to operate.
What Is Flexoelectricity and Why Ice Matters
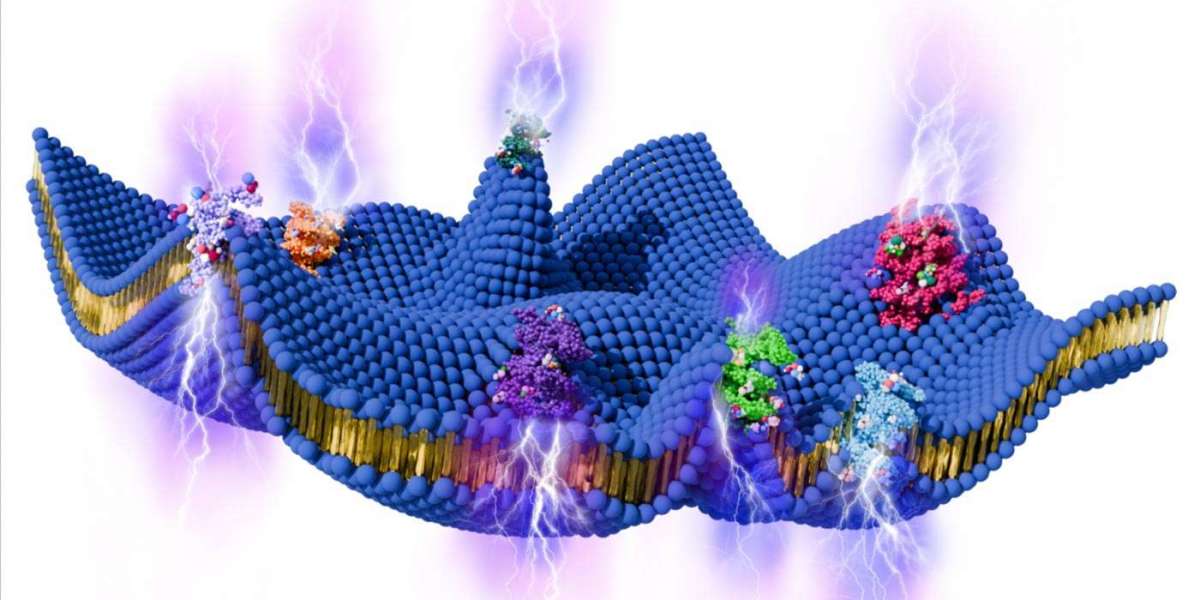
Unlike piezoelectric materials, which generate electricity when compressed, ice does not normally produce an electric charge under pressure. However, scientists have discovered that ice can generate electricity through flexoelectricity, a phenomenon where an electric charge appears when a material is unevenly deformed or bent.
This effect was first observed in pure ice, but the electrical output was extremely weak. While scientifically interesting, it was not strong enough for practical applications.
How Adding Salt Dramatically Boosts Electricity Generation
Researchers found that introducing common salt (sodium chloride) into ice changes everything. When ice contains about 25% salt, its ability to generate electricity increases by a factor of 1,000 compared to pure ice.
This dramatic enhancement occurs because salty water becomes trapped along the microscopic boundaries between ice crystals. When the ice bends, water molecules and salt ions move from compressed regions toward stretched regions. This internal movement of charged particles creates an electric current, significantly amplifying the ice’s flexoelectric response.
At this level, salty ice approaches the performance of some piezoelectric materials already used in electronic devices.
Prototype Devices and Energy Harvesting Potential
Using this principle, researchers have already developed prototype devices capable of converting the mechanical bending of ice into usable electrical energy. While these prototypes are still experimental, they demonstrate that salty ice can function as an energy-harvesting material rather than just a scientific curiosity.
Such devices could be produced directly in cold environments, using locally available water and salt, reducing the need for complex manufacturing or material transport.
Applications in Extreme and Remote Environments
One of the most promising aspects of salty ice electricity generation is its suitability for extreme conditions. Polar regions, glaciers, and high-altitude environments are notoriously difficult places to deploy conventional electronics.
Salty ice could enable:
Low-cost environmental sensors embedded in ice or snow
Temporary power sources for scientific instruments
Self-powered monitoring systems in polar research stations
Beyond Earth, this phenomenon may also help scientists understand electrical activity in icy extraterrestrial environments, such as Jupiter’s moon Europa or Saturn’s moon Enceladus.
Limitations and Scientific Challenges
Despite its promise, salty ice is not without drawbacks. Research shows that its efficiency decreases after many cycles of bending, and its overall power output remains lower than that of the most advanced commercial piezoelectric materials.
These limitations mean salty ice is unlikely to replace existing energy technologies. Instead, it may fill a unique niche where sustainability, availability, and environmental compatibility are more important than high power output.
Conclusion: A Small Discovery With Big Implications
The discovery that salty ice can generate electricity reshapes how we think about energy in cold environments. By combining simple materials with fundamental physics, researchers have uncovered a sustainable, low-cost way to harvest energy where few alternatives exist.
While challenges remain, salty ice highlights how nature-inspired solutions can support future clean technologies and deepen our understanding of both Earth’s icy regions and distant frozen worlds. Sometimes, innovation is not about finding new materials, but about seeing familiar ones in an entirely new light.
Key Points Summary
Ice can generate electricity through flexoelectricity when unevenly bent
Adding salt boosts this effect by up to 1,000 times
Salty ice approaches the performance of some piezoelectric materials
Ideal for sensors and energy harvesting in extreme cold environments
Offers insights into natural and extraterrestrial icy systems
advertisement
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Can ice really generate electricity?
Yes. When ice is unevenly deformed, it can generate electricity through flexoelectricity, especially when mixed with salt.
Why does salt make ice more electrically active?
Salt creates mobile ions and salty water at ice crystal boundaries, which move during bending and generate electric current.
Is salty ice better than piezoelectric materials?
Not overall. While impressive, salty ice still produces less power and degrades faster than advanced piezoelectric materials.
Where could this technology be used?
In polar regions, glaciers, remote sensing applications, and possibly space exploration involving icy moons.
Is salty ice environmentally friendly?
Yes. It is made from abundant, low-cost, and sustainable materials like water and salt.
Sources :
ICN2 – Research on salty ice and flexoelectric electricity generation
https://icn2.cat/en/news/5508-salty-ice-a-new-way-to-generate-electricity-in-extreme-conditions-4
Thank you !