Image credit and Source:
Credits: NASA, ESA, Elizabeth Wheatley (STScI); Science: Andrea Dupree (CfA)
Source: space.com (Link)
Hubble Space Telescope Discoveries: How Hubble Revealed Betelgeuse’s Hidden Companion Star
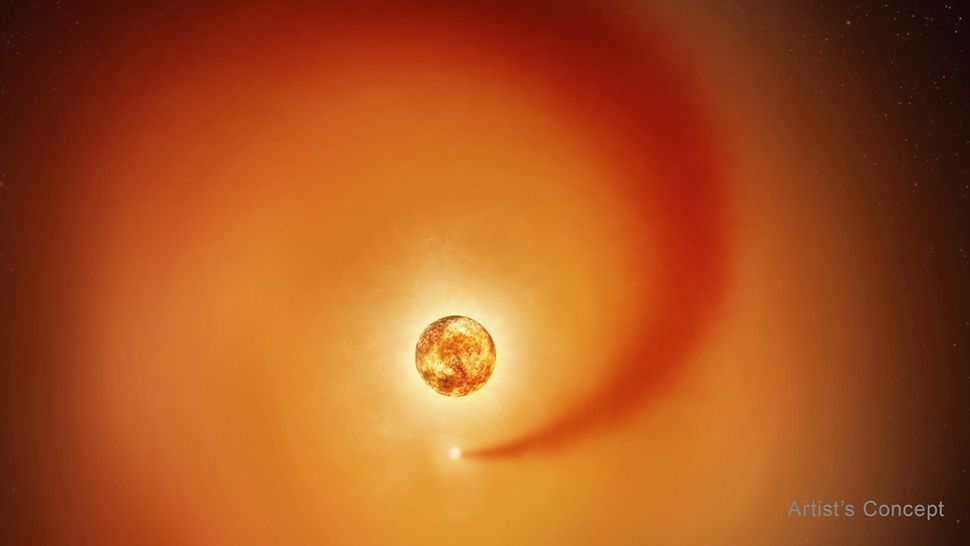
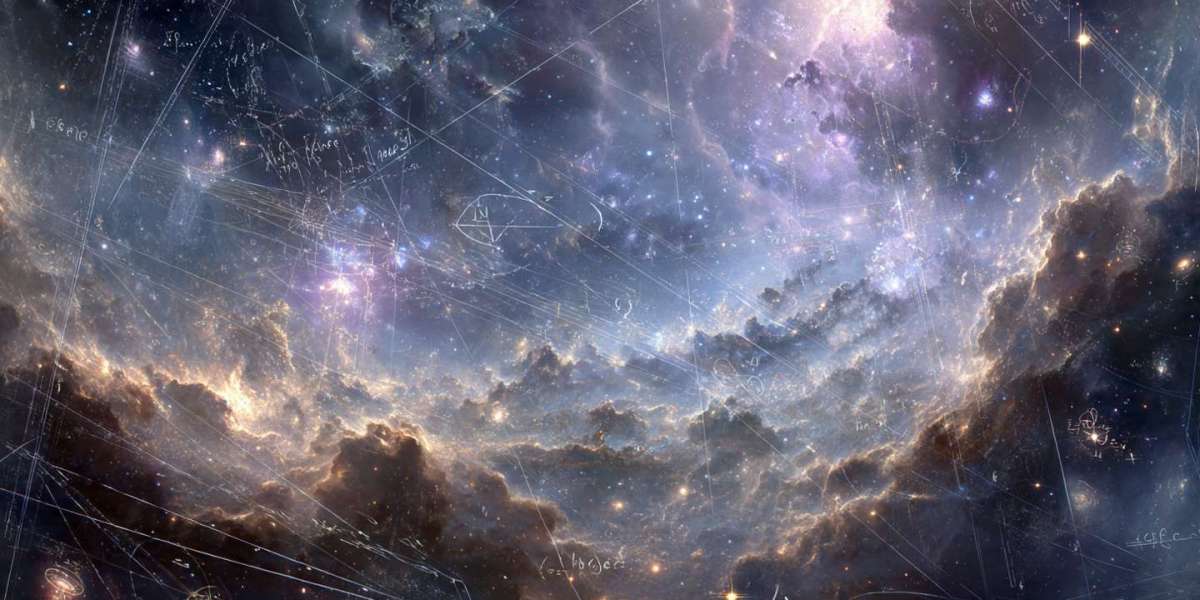
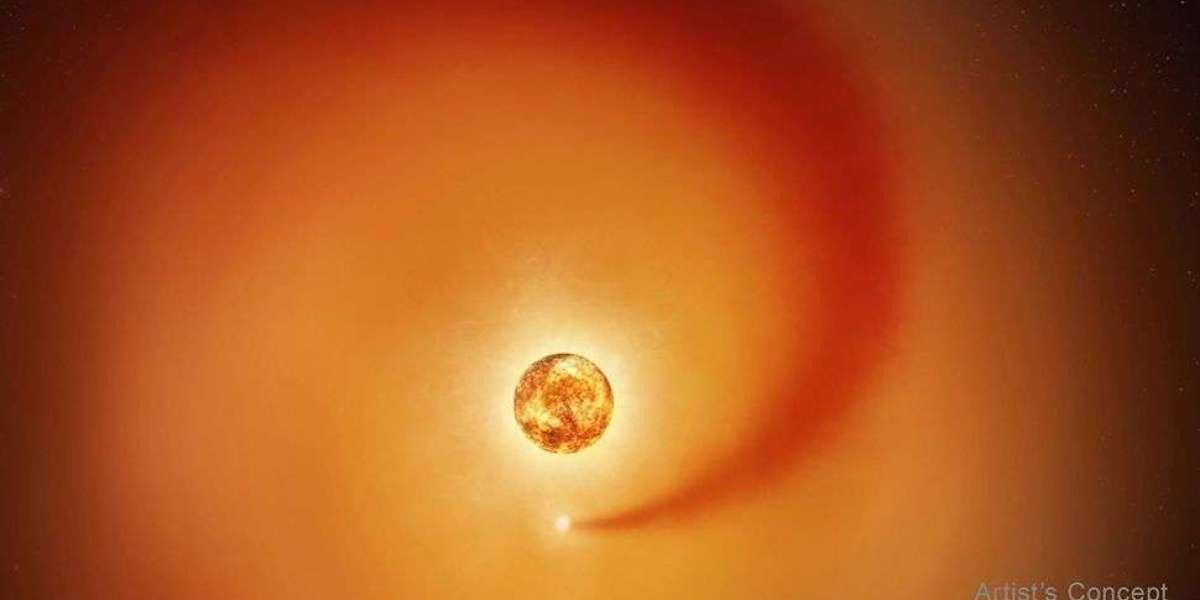
This artist’s concept shows the red supergiant star Betelgeuse and an orbiting companion star. The companion, which is orbiting clockwise from this point of view, generates a dense wake of gas that expands outward. It is so close to Betelgeuse that it is passing through the extended outer atmosphere of the supergiant. The companion star is not to scale; it would be a pinprick compared to Betelgeuse, which is hundreds of times larger. The companion’s distance from Betelgeuse is to scale relative to the diameter of Betelgeuse. (Image credit: NASA, ESA, Elizabeth Wheatley (STScI); Science: Andrea Dupree (CfA))
image Source: space.com (Link)
Introduction: The Hubble Space Telescope and Stellar Mysteries
Since its launch in 1990, the Hubble Space Telescope has transformed our understanding of the universe. Orbiting above Earth’s atmosphere, Hubble provides crystal-clear views of distant galaxies, nebulae, and stars, helping astronomers answer some of the biggest questions in astronomy. One of its most fascinating recent contributions involves Betelgeuse, a famous red supergiant star, where Hubble observations have helped confirm the existence of a hidden companion star and revealed how massive stars evolve over time.
Key Points
The Hubble Space Telescope confirmed a hidden companion star orbiting Betelgeuse.
The companion, named Siwarha, creates a dense wake in Betelgeuse’s atmosphere.
This wake becomes visible every six years when the stars align with Earth.
The discovery helps explain Betelgeuse’s unusual dimming and brightening.
Observations provide valuable insight into how massive stars evolve and lose material.
advertisement
Why Betelgeuse Fascinates Astronomers
Betelgeuse, located in the constellation Orion, stands out as one of the brightest and largest stars visible to the naked eye. Unlike most stars, which appear as simple points of light, Betelgeuse is both close enough and large enough for scientists to study its surface and atmosphere in detail.
For years, astronomers have observed puzzling behavior from Betelgeuse. The star frequently dims and brightens, and its outer layers appear unstable. These changes sparked debate within the scientific community, with some researchers suggesting that an unseen companion star might be influencing Betelgeuse’s appearance.
Hubble Confirms a Hidden Companion
In July 2025, astronomers identified a companion star within Betelgeuse’s outer atmosphere. This companion, named Siwarha, had long been suspected but lacked direct evidence. New observations from the Hubble Space Telescope, combined with data from ground-based observatories, finally provided confirmation.
According to researchers, Hubble detected a distinct “wake” created as Siwarha moves through Betelgeuse’s extended atmosphere. This wake is made of denser material than the surrounding gases, allowing scientists to trace the companion’s path and confirm its existence.
Andrea Dupree of the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian explained that this finding offers direct evidence supporting a theory that had been gaining attention for years. The discovery gives astronomers an unprecedented opportunity to observe how a giant star responds to the gravitational influence of a nearby companion.
The Science Behind the Stellar Wake
Every six years, Siwarha passes between Betelgeuse and Earth. During this alignment, its dense trail becomes visible in Hubble’s data, subtly altering the spectrum of light emitted by elements in Betelgeuse’s atmosphere. Scientists compare this effect to the wake created by a boat moving through water, where ripples reveal motion that would otherwise remain hidden.
By analyzing these spectral changes, astronomers can study how material moves and reshapes itself around a red supergiant star. This insight is critical for understanding how massive stars lose material, change over time, and ultimately explode as supernovae.
Why This Discovery Matters
The confirmation of Siwarha’s wake goes beyond solving a single stellar mystery. It provides a real-time laboratory for studying stellar evolution. Observing Betelgeuse and its companion allows scientists to see how interactions between stars influence mass loss and structural changes, processes that play a key role in the life cycle of the universe’s most massive stars.
Future observations are already planned. Siwarha is expected to become visible again in 2027, offering astronomers another chance to refine their models and deepen our understanding of how giant stars behave in their final stages.
Conclusion: Hubble’s Continuing Legacy
The Hubble Space Telescope continues to prove its value decades after launch. By revealing the hidden companion of Betelgeuse and capturing the wake it leaves behind, Hubble has given humanity a front-row seat to stellar evolution in action. These discoveries not only explain the strange behavior of one famous star but also help scientists understand how massive stars live, change, and ultimately shape the cosmos. As Hubble and future space telescopes continue to observe the universe, each new finding brings us closer to understanding our place among the stars.
advertisement
FAQ
What is the Hubble Space Telescope?
Hubble is a space-based observatory launched in 1990 that studies stars, galaxies, and other cosmic objects without atmospheric interference.
Why is Betelgeuse important to astronomers?
Betelgeuse is a nearby red supergiant star whose size and brightness allow detailed study of stellar behavior.
What is Siwarha?
Siwarha is a companion star orbiting within Betelgeuse’s outer atmosphere, recently confirmed through Hubble observations.
How did Hubble detect the companion star?
Hubble observed a dense wake in Betelgeuse’s atmosphere caused by the companion’s movement, visible through spectral changes.
Why does this discovery matter?
It helps scientists understand stellar evolution, mass loss, and how massive stars eventually become supernovae.
Sources:
Space.com – Report on Hubble observations confirming Betelgeuse’s hidden companion and its stellar wake
https://www.space.com/astronomy/stars/hubble-telescope-spies-wake-of-supergiant-beutelgeuses-hidden-companion-star
Thank you !